Is a high-protein diet harmful to your health?
Protein is an essential nutrient and is vital to your health. It is used to build muscles, skin, hair, and nails.
Prolonged intake of a large amount of protein has been associated with potential dangers, such as bone mineral loss and kidney damage.
I wanted to find out if this is true or not.
For healthy individuals, there is little evidence that high protein intake is dangerous.
Research shows that unless you have already an existing kidney disease, an extreme protein diet has no adverse effects on kidneys.
Research has also shown that there appears to be no relation between protein intake and bone fracture risk. On the other hand, consuming insufficient protein can even be detrimental to the bones.
The protein requirement differs per person
People who do a lot of strength sports need more protein than people who don’t exercise. They have more muscles and muscles to consume a lot of protein. For athletes with high protein intake, it is important to have sufficient intake of other nutrients to support the training load.
– An adult person who does not exercise needs an average of 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day.
– Endurance athletes need an average of 1.2 to 1.4 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day
– Strength athletes need an average of 1.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day
Complete vs incomplete proteins
What is the difference between complete and incomplete proteins?
Proteins can differ greatly in amino acid profile. Our body breaks down proteins into these separate amino acids and uses these released building materials to make new proteins where necessary. There are a total of twenty-two different amino acids, nine of which are essential. These are considered essential because the body cannot produce them itself.
Nutrition is the only way to get these essential amino acids. It is also the case that all essential amino acids must be present in order to produce new proteins. For this reason, we consider all foods that contain all essential amino acids as “complete.” These foods are most desirable for muscle growth and recovery. Incomplete protein sources can also be combined with each other to obtain a complete amino acid profile.
Non-essential amino acids can be made by humans and so is not essential to the human diet.
Non-essential amino acids can become essential under certain circumstances when the rate at which the body produces a certain amino acid falls short to meet the need. Such an amino acid is then called “semi-essential” or “conditionally essential”. Examples of such conditions can be rapid growth, surgery, or strenuous exercise.
Essential
|
Non-essential
|
Semi-essential
|
|
Fenylalanine |
Alanine |
Arginine |
|
Histidine |
Asparaginezuur |
Asparagine |
|
Isoleucine |
Cysteïne |
Glutamine |
|
Leucine |
Cystine |
Glycine |
|
Lysine |
Glutaminezuur |
Proline |
|
Methionine |
Hydroxyproline |
Serine |
|
Threonine |
Tyrosine |
|
|
Tryptofaan |
|
|
|
Valine |
|
|
– Complete proteins: e.g. beef, chicken, fish, turkey, pork, dairy, soy, quinoa, seitan, and buckwheat,
– Incomplete protein: e.g. nuts, seeds, rice, beans, and grains
Make sure you are not completely dependent on one protein source, and that you get proteins from different sources. This way you get an extensive package of amino acids.

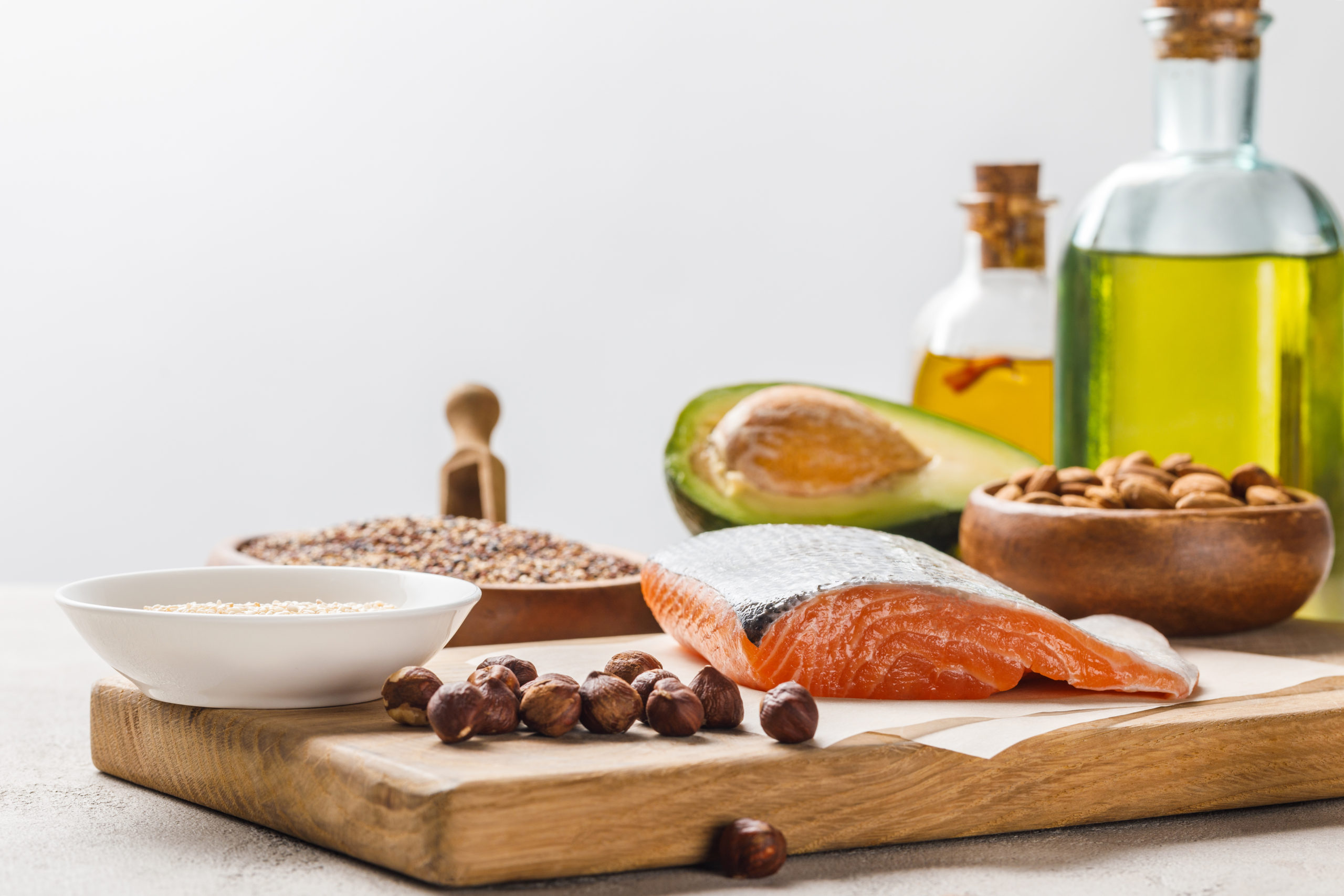
Protein-rich diet and weight loss
With a high protein diet, the increased satiety plays the biggest role in weight loss. Proteins are the most satiating macronutrient. The advantage of a high-protein diet is that the lean body mass is largely preserved and that especially fat tissue is lost. However, it remains unclear if high-protein diets can work for the long term.
If your goal is to burn body fat and prevent muscle loss, then you should aim for 0.8 to 1.3 grams of protein per kg of body weight.
While eating more protein than what’s recommended is not necessarily bad for you, if the excess protein in a diet is contributing to excess calories, it can contribute to weight gain.
Foods that are high in protein include:
- Meats: beef, chicken, fish, turkey, and lamb
- Milk and cheese, yogurt, cottage cheese, and cream cheese
- eggs
- Peanut butter (with bread or crackers)
- Dried beans and peas (with bread, cornbread, rice)
Print the free reference chart: “Foods high in Proteins” that you will find at the bottom of this article.
Benefits of a high protein diet
- Proteins reduce the appetite and stimulate the production of an appetite suppressant hormone.
- Proteins digest more slowly, which means you feel full longer.
- Increase in metabolism: your metabolism increases in the first few weeks, because your body switches to burning carbohydrates into proteins. This will burn more calories and therefore more fat.
- Hardly any loss of muscle mass: if you go on a heavy diet your body will lack energy and it can start to burn muscle mass. This happens much less with the protein diet. You are not hungry and get all the energy you need.
- Belly Fat Loss: Following the protein diet, you’ll lose belly fat that is healthier faster.
Disadvantages of a high-protein diet
- The most important thing to keep in mind is that you follow a balanced diet. Make sure you still get enough fats, fiber, and carbohydrates.
- Another point to consider is the type of protein-rich products you choose. Some protein-rich products are high in saturated fat and calories.
- The lack of carbohydrates can cause a headache in the first days.
- Higher protein intake causes bad breath. Proteins remain in the mouth and on the tongue and are broken down by bacteria.
- You may experience more acne during a protein diet
- Eating more protein can cause flatulence.
- A high-protein diet can be more expensive than your normal diet.
- Eating a lot of animal protein is harmful to the environment. Eating legumes is less of a burden on the environment.
Despite the persistent myth, a high protein diet is not harmful to healthy adults. There is no scientific evidence to support these vague claims about eating too much protein.
2 Comments
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Supplements Are Really Beneficial For Your Body 2021 - Transformelle - […] Protein is an additional essential nutrient. Your body utilizes healthy protein to:– Build as well as Repair Muscular Tissue.–…
- How your brain influences your health - Transformelle - […] everyone realizes today, the significance of healthy protein in our diet. Healthy protein directly influences our muscle mass, tissues…
- Metabolism: What Is It, And Can We Control It? - Transformelle - […] metabolic process, but studies suggest the best approach is to incorporate appropriate healthy protein consumption with weightlifting, which enhances muscle mass…
- How to use Protein Powder and is it Right for You? - Transformelle - […] numerous brand names to choose from and the fairly high price per serving, buying a protein powder can […]
- Holistic Living and Alternative Therapies for Wellness - Transformelle - […] usage of foods that are exceptional resources of the macronutrients which include fats, healthy protein as well as […]
- Your gut health and how to maintain the balance of good and bad bacteria | Transformelle - […] – Protein.– Healthy and balanced fats.– Carbohydrates.– Fiber.– Vitamins.– Minerals.– Water.– Antioxidants. […]
Submit a Comment












whoah this weblog is excellent i love studying
your articles. Stay up the good work! You know, lots of persons are looking round for this info, you could help them greatly.
Wonderful web site. Plenty of useful info here.
I am sending it to several friends ans additionally sharing in delicious.
And naturally, thanks on your effort! asmr 0mniartist